What Are Birth Control Pills?
Birth control pills are oral contraceptives containing hormones like estrogen and progestin to prevent pregnancy. They work by stopping ovulation, thickening cervical mucus, and thinning the uterine lining. Beyond contraception, they also help manage conditions like irregular periods, acne, and PCOS.
Myth: Birth Control Pills Lead to Infertility
A common myth is that using birth control pills causes permanent infertility. However, this is untrue.
• Fertility Resumes Quickly: Most women regain fertility within weeks to months after stopping the pill.
• Temporary Effects Only: Any delay in ovulation is temporary and does not indicate infertility.
• Underlying Issues: Fertility challenges after discontinuing the pill are usually due to pre-existing conditions like PCOS or age-related factors.
Fact Check:
Scientific studies confirm that birth control pills do not cause infertility and may even protect fertility by preventing certain conditions.
Fact: Birth Control Pills Do Not Impact Future Fertility
Contrary to popular myths, birth control pills do not cause long-term infertility. They are designed to temporarily suppress ovulation, preventing pregnancy during use. Once you stop taking the pill, your natural menstrual cycle typically resumes within a few months, and ovulation can occur as early as the next cycle for many women. Some individuals might experience a short delay in resuming regular cycles, especially if they had irregular periods before starting the pill, but this delay is not a sign of infertility.
Scientific research has repeatedly confirmed that birth control pills have no lasting impact on a woman’s ability to conceive. If cycles remain irregular or absent for an extended period after discontinuing the pill, it’s advisable to consult an infertility specialist in Visakhapatnam to rule out any underlying conditions.
Related content: How To Enhance Fertility Journey With Lifestyle Changes?
Factors That Can Impact Fertility
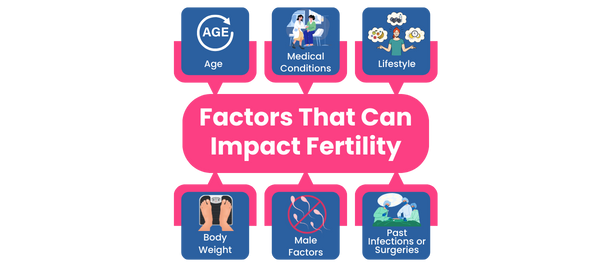
While birth control pills do not affect long-term fertility, other factors can influence one’s ability to conceive:
1. Age: Fertility naturally declines with age, particularly after 35, due to a decrease in the quantity and quality of eggs.
2. Medical Conditions: Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, and thyroid disorders can affect ovulation and overall fertility.
3. Lifestyle: Habits like smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, a poor diet, and high levels of stress can significantly impact reproductive health.
4. Body Weight: Both underweight and overweight individuals may experience hormonal imbalances that disrupt ovulation.
5. Male Factors: Male infertility, including low sperm count, poor motility, or structural issues, also plays a role in conception challenges.
6. Past Infections or Surgeries: Pelvic infections or surgeries involving the reproductive organs may lead to scarring or blockages, potentially affecting fertility.
How Birth Control Pills Work
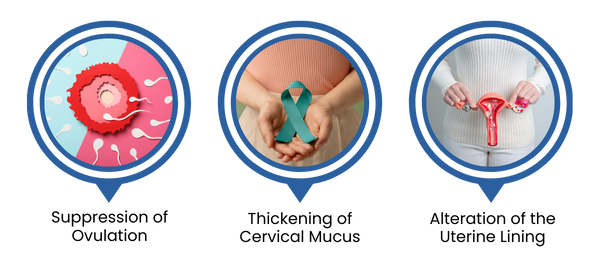
Birth control pills, also known as oral contraceptives, work by preventing pregnancy through hormonal regulation. They primarily contain synthetic versions of hormones like estrogen and progestin, which mimic the natural hormones in a woman’s body. Here’s how they function:
a. Suppression of Ovulation:
The pills inhibit the release of eggs from the ovaries (ovulation). Without an egg to fertilize, pregnancy cannot occur.
b. Thickening of Cervical Mucus:
The hormones thicken the mucus in the cervix, making it difficult for sperm to reach the egg.
c. Alteration of the Uterine Lining:
Birth control pills thin the lining of the uterus (endometrium), making it less likely for a fertilized egg to implant and grow.
By combining these mechanisms, birth control pills ensure effective prevention of pregnancy when taken as prescribed.
Facts About Birth Control and Fertility
a. Birth Control Pills Do Not Cause Permanent Infertility
One of the most common myths is that long-term use of birth control pills leads to infertility. Scientific studies have debunked this. Once you stop taking the pill, your fertility typically returns to its natural state. Most women ovulate within a few weeks or months after discontinuing the pill.
b. Temporary Delay in Ovulation
After stopping birth control, some women may experience a brief delay in ovulation. This is a normal adjustment period as the body regulates its natural hormonal cycle. It does not indicate infertility.
c. No Evidence of Long-Term Harm
Research has consistently shown that birth control pills do not have a long-term negative impact on a woman’s ability to conceive. Women who have used oral contraceptives have the same fertility rates as those who have never used them.
d. Other Factors Influence Fertility
If you experience difficulty conceiving after stopping birth control, other factors such as age, underlying health conditions, or lifestyle may play a more significant role than past contraceptive use.
e. Health Benefits of Birth Control Pills
In addition to preventing pregnancy, birth control pills offer several health benefits, including regulating menstrual cycles, reducing symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and lowering the risk of ovarian and endometrial cancers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, birth control pills do not cause infertility in the future. Once you stop using them, your fertility usually returns to normal within a few months. The idea that birth control pills lead to permanent infertility is a myth.
If you experience difficulty conceiving after stopping, other factors like age or health conditions may play a role. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and consulting experienced Infertility Doctors in Vizag can help support fertility. Understanding the truth about birth control can help you make informed decisions about your reproductive health.
