Best IVF Treatment in Vizag, Andhra Pradesh
What is IVF In-Vitro Fertilization ?
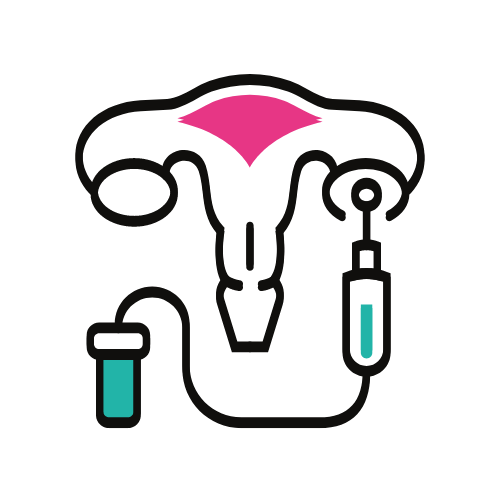
IVF stands for in vitro fertilization. It is a procedure in which eggs are removed from a woman’s ovaries and fertilized with sperm in a laboratory. The fertilized egg, called an embryo, is then transferred to the woman’s uterus with the intention of establishing a successful pregnancy.
IVF is needed when couples are unable to conceive naturally due to factors such as infertility, blocked fallopian tubes, or genetic disorders.
What is the process of IVF Treatment?
In-vitro fertilization (IVF) is a medical procedure in which an egg is fertilized by sperm outside of the body, in a laboratory dish. The process typically involves the following steps:
1) Stimulation of egg production: The woman takes medication to stimulate the production of multiple eggs.
2) Egg retrieval: The eggs are retrieved from the woman’s ovaries using a procedure called transvaginal ultrasound aspiration.
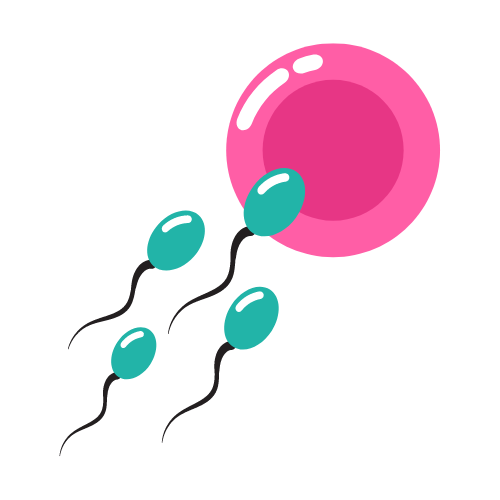
3) Fertilization: The eggs are fertilized with sperm in a laboratory dish, either by placing the sperm and eggs together and allowing them to fertilize naturally (called “conventional IVF”), or by injecting a single sperm directly into an egg (called “ICSI“).
4) Embryo culture: The fertilized eggs, now called embryos, are grown in the laboratory for 2 to 6 days.
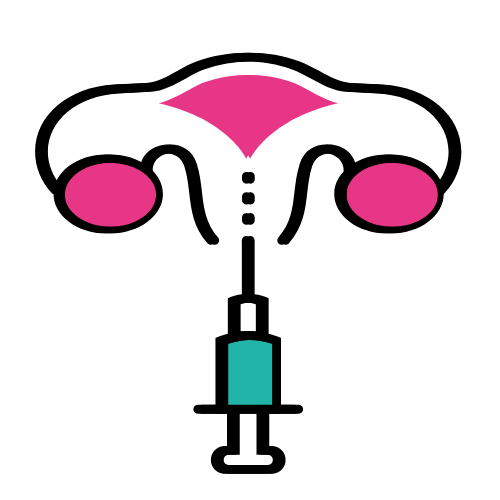
5) Embryo transfer: One or more embryos are transferred to the woman’s uterus, with the goal of establishing a pregnancy.
6) Luteal Support and Pregnancy Test : After embryo transfer, the woman is given medication to support the implantation of the embryo and will take a pregnancy test two weeks later.
7) Cryopreservation : Any remaining embryos that are not transferred can be frozen for future use.
When is IVF procedure recommended?
IVF is typically recommended when other forms of infertility treatment, such as ovulation induction or artificial insemination, have been unsuccessful. It may also be recommended in cases where the cause of infertility is known to be related to the fallopian tubes, uterus, or sperm. IVF may be an option for couples who have been trying to conceive for at least one year without success, or for women who have irregular menstrual cycles or have been diagnosed with conditions such as endometriosis or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).